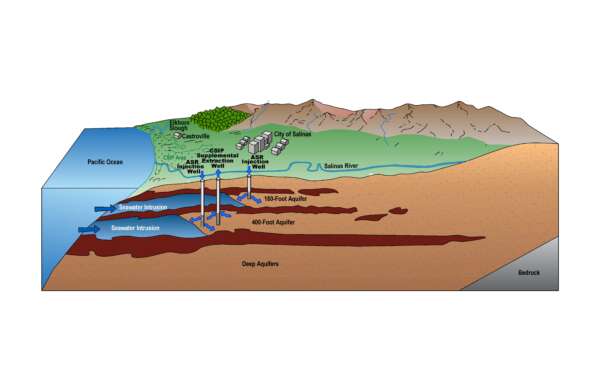
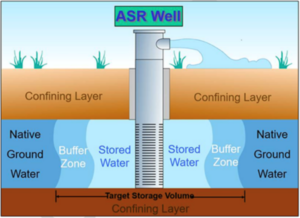
One method to potentially address seawater intrusion is injecting fresh water into aquifers on the landward side of the intrusion. This raises groundwater elevations and helps push back the seawater. The Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency (SVBGSA) has evaluated this method in a Preliminary Feasibility Study of Aquifer Storage and Recovery (ASR) Project Concepts to Address Seawater Intrusion (January 2025). The ASR report can be found here.
This study examines a project concept within the 180/400-Foot Aquifer Subbasin and Monterey Subbasin Groundwater Sustainability Plans, known as the Seasonal Release with ASR project concept. The study also has led to the development of a new project, the New Diversion of Winter High Flows for ASR (Alternatives 1 and 1A).
These ASR project concepts aim to reduce seawater intrusion while ensuring a sustainable water supply for the Castroville Seawater Intrusion Project (CSIP) area by:
- Increasing surface water diversions for recharge during the wet season
- Injecting diverted surface water inland of the seawater-intruded area to raise groundwater elevations
- Partially recovering injected water during the growing season to supplement CSIP supplies and reduce reliance on native groundwater
The study includes a summary report with key findings and four technical memoranda:
- TM-1: Assesses physical and operational constraints, considering existing infrastructure such as the Nacimiento and San Antonio Reservoirs, the Salinas River Diversion Facility, and CSIP, while identifying new infrastructure needs.
- TM-2: Reviews permitting and regulatory requirements, including water rights.
- TM-3: Summarizes available water quality data and recommends a sampling plan for further treatment analysis.
- TM-4: Presents groundwater flow modeling results.
This study was conducted in coordination with the Monterey County Water Resources Agency.