About Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency
In 2017, local GSA-eligible entities jointly developed the Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency (SVBGSA) to develop Groundwater Sustainability Plans (GSPs) and manage groundwater in the Salinas Valley under California’s Sustainable Groundwater Management Act. The SVBGSA represents a range of interests including agriculture, cities, public utility, disadvantaged communities , County, and environmental stakeholders. The Salinas Valley Groundwater Basin includes 9 subbasins, 6 of which fall partially or entirely within the jurisdiction of the SVBGSA. The Department of Water Resources designated all 6 SVBGSA subbasins as either high or medium priority basins. In addition, it designated the 180-400-Foot Aquifer Subbasin as a critically overdrafted basin. In 2020, SVBGSA completed the GSP for the 180/400-Foot Aquifer Subbasin. In 2022, SVBGSA completed GSPs with partner GSAs for its remaining 5 subbasins: the Eastside Aquifer Subbasin, the Forebay Aquifer Subbasin, the Upper Valley Aquifer Subbasin, the Langley Area Subbasin, and the Monterey Subbasin.
The Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency is tasked with the ambitious goal of developing a comprehensive groundwater sustainability plan by 2020 and implementing the plan to achieve basin sustainability by 2040. Read the implementation timeline.
The Agency’s 11-member Board is comprised of diverse interests from across the Salinas Valley.
Salinas Valley GSA Overview Fact Sheet
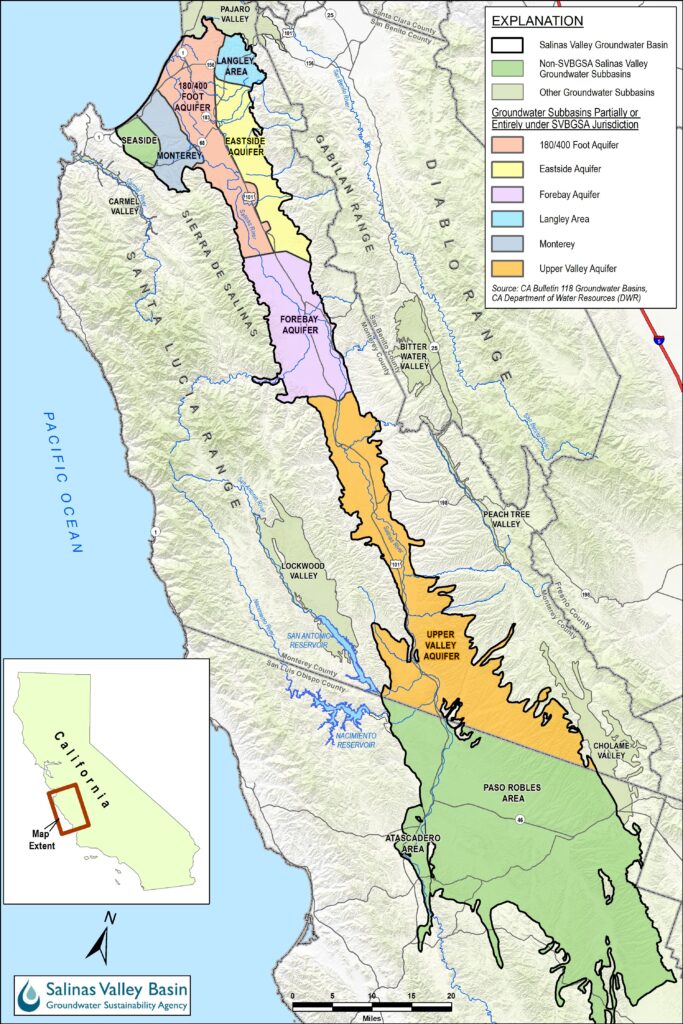
Salinas Valley Basin Map
Sustainable Groundwater Management Act Brochure
Formation of Groundwater Sustainability Agency (GSA) 2015-2017
2015: Stakeholder Issue Assessment Conducted
Local agencies and stakeholders worked with the Consensus Building Institute (CBI) to facilitate groundwater sustainability formation in the Salinas Valley Groundwater Basin. To kick this off, CBI conducted a Salinas Valley Groundwater Stakeholder Issue Assessment, which included interviews and surveys with key stakeholders.
The CBI Stakeholder Assessment Report outlined the following keys to success for the GSA formation planning process:
- Create a transparent, inclusive process that engages interested stakeholders,
- Design a governance structure that balances interests, supports a vibrant economy, manages groundwater sustainability, and meets state SGMA requirements.
2016-2017: Collaborative Work Group
The Collaborative Work Group was formed of stakeholders representing a broad range of interests, and met from March 2016 through April 2017 to develop recommendations on GSA formation in the Salinas Valley, including governance structure, voting, and legal structure. These recommendations resulted in the formation of the Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency in April 2017.
Sustainable Groundwater Management Act
What is the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA)?
In September 2014, California Governor Jerry Brown enacted legislation that sets forth a path to create local agencies to sustainably manage the state’s groundwater resources. This initiative, known as the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act, shifts planning and management of groundwater resources to newly formed Groundwater Sustainability Agencies, made up of local agencies (cities, counties, water districts) and requires development of Groundwater Sustainability Plans by 2020 for priority basins. The state designated Salinas Valley as a priority basin.
For more information on SGMA, visit groundwater.ca.

How does a Groundwater Sustainability Agency (GSA) form?
What is the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act (SGMA)?
In September 2014, California Governor Jerry Brown enacted legislation that sets forth a path to create local agencies to sustainably manage the state’s groundwater resources. This initiative, known as the Sustainable Groundwater Management Act, shifts planning and management of groundwater resources to newly formed Groundwater Sustainability Agencies, made up of local agencies (cities, counties, water districts) and requires development of Groundwater Sustainability Plans by 2020 for priority basins. The state designated Salinas Valley as a priority basin.
For more information on SGMA, visit groundwater.ca.
View Factsheets:
What is a GSA and Who Decides
Process for Forming a GSA in Salinas Valley
The first step in SGMA implementation was to form a Groundwater Sustainability Agency by June 30, 2017. Under SGMA, an agency or combination of local agencies may form a GSA by using any of the following methods: a joint powers authority (JPA) agreement, or a memorandum of agreement (MOU) or other legal agreement.
From 2015 to 2017, stakeholders in the Salinas Valley worked collaboratively to develop recommendations on formation of the Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency (SVBGSA) as a joint powers authority.
What entities are eligible to serve as a GSA?
SGMA provides that a local agency, a combination of local agencies, or a county may establish a GSA. Specifically, a local agency is defined as any local public entity that has water supply, water management, or land use responsibilities within a groundwater basin. In short, any local agency or combination of local agencies overlying a groundwater basin can elect to be a GSA. A water corporation regulated by the Public Utilities Commission or a mutual water company may participate in a GSA through a memorandum of agreement or other legal agreement. Non-agency parties can be incorporated into the decision-making process for the GSA through advisory bodies or by creating special provisions in the legal formation.
View the list of GSA-eligible agencies in the Salinas Valley.
SCO Reporting Websites
Every year, the Salinas Valley Basin Groundwater Sustainability Agency reports financial information to the State of California Controller’s Office. You can find yearly reported information on the SCO’s website:
- Government Financial Reports
SVBGSA Yearly Financials
Fiscal Year 2023
Fiscal Year 2022
- 2022 Audited Financial Statements (PDF)
- Fiscal Year 2022 Budget (PDF)
- 2022 SCO Financial Transactions Report (PDF)
Fiscal Year 2021
Fiscal Year 2020
- 2020 Audited Financial Statements (PDF)
- Fiscal Year 2020 Budget (PDF)
- 2020 SCO Financial Transactions Report (PDF)
Fiscal Year 2019
- 2019 Audited Financial Statements (PDF)
- Fiscal Year 2019 Budget (PDF)
- 2019 SCO Financial Transactions Report (PDF)
